Flood irrigation, also known as surface irrigation, is a traditional farming method used worldwide. It involves channeling water from a source, such as a river or reservoir, directly onto agricultural fields. While this method is time-tested, it comes with both benefits and challenges that farmers must carefully consider.
This article explores the pros and cons of flood irrigation and offers insights to help you decide if it’s suitable for your farming needs.
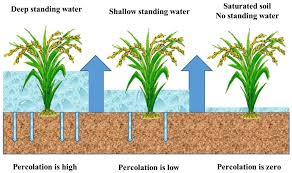
What is Flood Irrigation?
Flood irrigation involves directing water across a field, allowing it to soak into the soil naturally. The process relies on gravity to distribute water, making it one of the simplest and most accessible irrigation methods.
The Pros of Flood Irrigation
Flood irrigation offers several advantages that can benefit farmers in certain situations:
1. Cost-Effective Setup
- Low Initial Investment: Requires minimal equipment, such as ditches, gates, and canals.
- Affordable Maintenance: Simple systems mean fewer repair costs.
2. Simplicity and Accessibility
- Ease of Use: Does not require complex technology or skills to implement.
- No Dependence on Electricity: Ideal for areas without reliable power supply.
3. Soil Health Benefits
- Deep Soil Hydration: Ensures adequate moisture for deep-rooted crops.
- Salt Leaching: Excess water can help flush salts out of the soil, improving its quality.
4. Suitable for Specific Crops
- Works well with water-intensive crops such as:
- Rice
- Sugarcane
- Cotton
5. Environmental Advantages
- Groundwater Recharge: Excess water percolates into aquifers, replenishing underground reserves.
- Eco-Friendly Option: No reliance on synthetic equipment or energy-intensive systems.
The Cons of Flood Irrigation
Despite its benefits, flood irrigation has limitations that can impact its effectiveness:
1. Water Inefficiency
- High Water Usage: Large quantities of water are needed to flood fields adequately.
- Evaporation Loss: Open water channels are prone to evaporation.
2. Risk of Overwatering
- Waterlogging: Excess water can suffocate plant roots, reducing crop yield.
- Uneven Distribution: Fields with slopes or irregularities may experience patchy irrigation.
3. Soil and Environmental Challenges
- Soil Erosion: Rapid water flow can wash away fertile topsoil.
- Loss of Nutrients: Runoff can deplete soil nutrients.
4. Labor-Intensive
- Manual Management: Requires constant monitoring and adjustments to ensure even water flow.
- Field Preparation: Regular maintenance of ditches and canals is necessary.

Comparison Table: Pros vs. Cons of Flood Irrigation
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Affordable setup and maintenance | High water cost in water-scarce regions |
| Ease of Use | Simple and accessible | Labor-intensive management |
| Water Usage | Effective for water-rich areas | Inefficient in water-scarce areas |
| Soil Impact | Salt leaching and deep hydration | Risk of erosion and nutrient loss |
| Crop Suitability | Ideal for water-intensive crops | Not suitable for crops sensitive to overwatering |
Factors to Consider Before Choosing Flood Irrigation
Here are some key factors to help determine if flood irrigation is suitable for your farm:
- Water Availability:
- Ensure you have access to ample water, as this method requires significant quantities.
- Field Topography:
- Flat fields are more suitable for even water distribution.
- Crop Type:
- Select crops that thrive in wet conditions, such as rice or sugarcane.
- Climate:
- In arid or hot regions, water loss due to evaporation may be significant.
- Soil Quality:
- Check for drainage capacity to avoid waterlogging and soil erosion.
User Feedback: Real-Life Experiences
Positive Feedback
- “Flood irrigation has been the most economical option for my rice fields. It’s simple and effective for my large farm.” – Ravi, India
- “The ability to leach salts from the soil has been a game-changer for us in the desert region.” – Fatima, UAE
Negative Feedback
- “I struggled with waterlogging in my fields, which affected the yield of my vegetables.” – Jake, USA
- “Managing water flow during the rainy season is a challenge, leading to uneven irrigation.” – Maria, Brazil
Tips for Optimizing Flood Irrigation
To make flood irrigation more efficient, consider these strategies:
- Level Your Fields: Use grading tools to ensure flat surfaces for even water distribution.
- Install Gates and Check Dams: Control water flow effectively to prevent wastage.
- Recycle Runoff: Redirect excess water to nearby fields or storage reservoirs.
- Monitor Water Flow: Regularly check for leaks or blockages in canals.
- Incorporate Soil Amendments: Add organic matter to improve soil structure and water retention.

Conclusion
Flood irrigation is a valuable method for farmers, especially those in regions with abundant water resources and suitable crops. Its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and soil benefits make it an attractive option for large-scale farming.
However, its water inefficiency, labor-intensive nature, and potential environmental impact may limit its applicability in certain scenarios. By understanding the pros and cons and implementing best practices, farmers can maximize the benefits of flood irrigation while mitigating its drawbacks.
Ultimately, the suitability of flood irrigation depends on your farm’s unique conditions and needs.