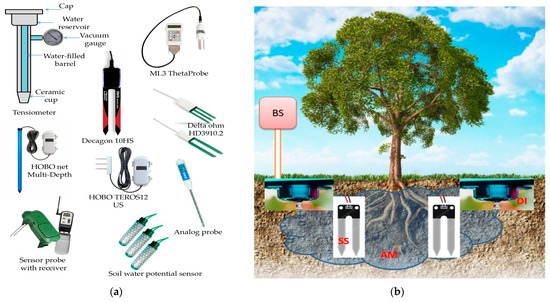
Flood irrigation is a popular method for watering crops, but it’s essential to understand the costs involved. From initial setup expenses to ongoing maintenance and water usage fees, calculating costs per acre is crucial for effective farm budgeting. This guide explores the various cost factors, provides a practical breakdown, and offers tips to manage expenses effectively.

Understanding Flood Irrigation Costs
Flood irrigation costs vary widely depending on factors like:
- Location: Costs differ between water-abundant and water-scarce regions.
- Field Size: Larger fields often benefit from economies of scale.
- Soil Type: Sandy soil may require more water, increasing costs.
- Crop Type: Water-intensive crops drive up irrigation needs.
Cost Breakdown for Flood Irrigation Per Acre
Here’s a general breakdown of costs associated with flood irrigation:
1. Initial Setup Costs
- Land Preparation:
- Leveling fields for even water distribution: $50–$150 per acre.
- Irrigation Infrastructure:
- Canals, ditches, and gates installation: $200–$500 per acre.
2. Water Costs
- Water Source:
- Cost of accessing water from rivers or reservoirs.
- Estimated cost: $30–$100 per acre annually.
3. Operation and Maintenance
- Labor:
- Monitoring water flow and maintaining canals: $20–$50 per acre annually.
- Repairs:
- Fixing leaks or damaged gates: $10–$30 per acre annually.
4. Energy Costs (if applicable)
- Pumping water (if required): $50–$120 per acre annually.
Table: Estimated Flood Irrigation Costs Per Acre
| Cost Component | Low Estimate ($) | High Estimate ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Land Preparation | 50 | 150 |
| Infrastructure Installation | 200 | 500 |
| Water Usage | 30 | 100 |
| Labor and Maintenance | 20 | 50 |
| Energy (if applicable) | 50 | 120 |
| Total Annual Cost | 350 | 920 |
Factors Influencing Costs
1. Geographical Location
- Water Availability:
- Costs are lower in water-rich areas compared to arid regions.
2. Field Characteristics
- Slope and Topography:
- Flat fields reduce preparation costs.
- Soil Permeability:
- Sandy soil requires more water, increasing usage costs.
3. Crop Requirements
- Water-intensive crops like rice incur higher costs than drought-tolerant crops like wheat.
4. Technology Use
- Automation:
- Adding automated gates increases setup costs but reduces labor expenses.
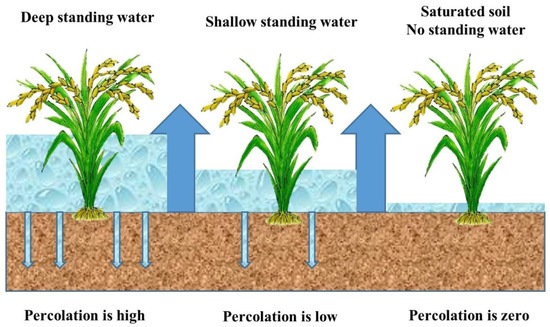
Real-Life Feedback from Farmers
Positive Experiences
- “Investing in proper land leveling drastically reduced water waste and costs.” – Ahmed, Egypt
- “Installing automated gates initially cost more, but it saved us significant labor costs in the long run.” – Lisa, USA
Challenges Highlighted
- “In dry seasons, the cost of purchasing additional water skyrockets.” – Manoj, India
- “Maintaining canals is labor-intensive and adds to annual expenses.” – Carlos, Mexico
Tips for Budgeting and Cost Management
1. Conduct a Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Compare flood irrigation with other methods like drip irrigation to determine feasibility.
2. Invest in Land Leveling
- Even fields minimize water usage and improve efficiency.
3. Optimize Water Usage
- Install flow meters to monitor and reduce water waste.
4. Automate Where Possible
- Use automated gates to lower labor costs and ensure consistent water flow.
5. Plan for Seasonal Variability
- Account for potential increases in water costs during dry periods.
Flood Irrigation vs. Other Irrigation Methods
| Aspect | Flood Irrigation | Drip Irrigation | Sprinkler Irrigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Low to Moderate | High | High |
| Water Efficiency | Moderate to Low | High | Moderate |
| Maintenance | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Crop Suitability | Water-intensive crops | Broad range of crops | Broad range of crops |

Conclusion
Flood irrigation can be a cost-effective solution for farms with access to abundant water and suitable field conditions. However, it’s crucial to factor in the initial setup, water usage, and ongoing maintenance costs to create an accurate budget. By investing in land preparation, optimizing water use, and considering automation, farmers can reduce expenses while maintaining productivity.
This practical guide provides the tools and insights to budget effectively and make informed decisions about flood irrigation.