As the world grapples with climate change, population growth, and resource scarcity, sustainable farming has become more critical than ever. These innovative practices not only ensure food security but also preserve the environment for future generations. Here are the top 10 sustainable farming practices to adopt in 2025:
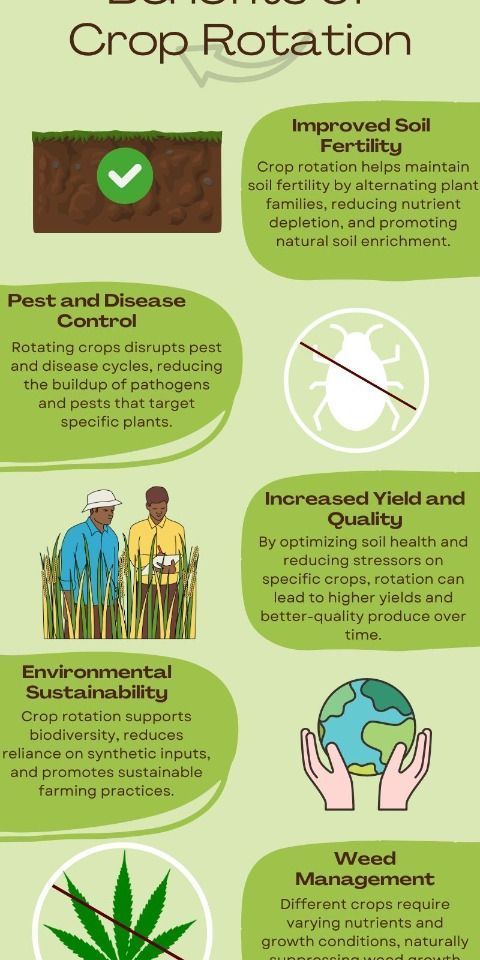
1. Crop Rotation and Diversity
Why it matters:
- Reduces soil nutrient depletion.
- Breaks pest and disease cycles.
- Improves overall soil health.
How to implement:
- Alternate crops annually or seasonally.
- Integrate leguminous plants (like beans) to fix nitrogen in the soil.
- Cultivate a mix of crops rather than monocultures.
Example:
| Year | Crop 1 | Crop 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | Corn | Soybeans |
| 2025 | Wheat | Clover |
| 2026 | Barley | Peas |
2. Conservation Tillage
Why it matters:
- Minimizes soil erosion.
- Retains soil moisture.
- Enhances organic matter content.
Key practices:
- Use reduced-till or no-till methods.
- Leave crop residues on fields.
- Employ specialized equipment to disturb the soil minimally.
3. Agroforestry
Why it matters:
- Combines agriculture and forestry for mutual benefits.
- Provides shade, windbreaks, and habitat for biodiversity.
- Sequesters carbon and improves soil structure.
Practical examples:
- Planting fruit or nut trees alongside crops.
- Integrating shrubs and hedgerows.
| Agroforestry Benefits | Description |
| Shade | Protects crops from excessive sunlight. |
| Windbreaks | Reduces crop damage from strong winds. |
| Soil Stabilization | Prevents erosion with tree roots. |

4. Drip Irrigation Systems
Why it matters:
- Reduces water wastage.
- Delivers water directly to plant roots.
- Enhances water-use efficiency.
Implementation tips:
- Install drip lines below the soil surface.
- Use timers to control watering schedules.
- Combine with rainwater harvesting systems.
5. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Why it matters:
- Reduces reliance on chemical pesticides.
- Maintains ecological balance.
- Improves crop yields by controlling pests naturally.
Components of IPM:
- Cultural controls: Crop rotation and sanitation.
- Biological controls: Introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs.
- Mechanical controls: Using traps and barriers.
- Chemical controls: As a last resort, applying pesticides judiciously.
6. Organic Farming
Why it matters:
- Avoids synthetic chemicals.
- Promotes soil and ecosystem health.
- Meets growing consumer demand for organic products.
Core principles:
- Use compost and natural fertilizers.
- Employ manual or biological weed control.
- Practice crop diversity.
| Organic Fertilizer Types | Benefits |
| Compost | Improves soil structure. |
| Manure | Adds essential nutrients. |
| Green Manure | Fixes nitrogen in the soil. |
7. Vertical Farming Why it matters:
- Maximizes land use efficiency.
- Reduces water usage by up to 90%.
- Allows year-round farming in controlled environments.
Key features:
- Multi-level growing systems.
- LED lighting for photosynthesis.
- Hydroponic or aeroponic systems.
Example layout:
| Level | Crop Type |
| 1 | Leafy greens |
| 2 | Strawberries |
| 3 | Tomatoes |
8. Precision Agriculture
Why it matters:
- Optimizes resource use.
- Enhances productivity and profitability.
- Reduces environmental impact.
Technologies involved:
- GPS-guided machinery.
- Drones for monitoring crops.
- Soil sensors to analyze nutrient needs.
9. Cover Cropping
Why it matters:
- Prevents soil erosion.
- Enhances soil fertility and structure.
- Suppresses weeds naturally.
Popular cover crops:
- Clover.
- Rye.
- Vetch.
Implementation:
- Plant cover crops after the main harvest.
- Incorporate into soil before the next planting.

10. Renewable Energy Integration
Why it matters:
- Reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- Decreases greenhouse gas emissions.
- Lowers long-term energy costs.
Options for farms:
- Solar panels for powering irrigation systems.
- Wind turbines for electricity.
- Biogas systems using animal waste.
Comparison of Renewable Energy Types:
| Energy Type | Benefits | Challenges |
| Solar | Low maintenance costs. | High initial setup. |
| Wind | Efficient in windy areas. | Requires open space. |
| Biogas | Utilizes waste. | Needs consistent input. |
Conclusion
Adopting these sustainable farming practices in 2025 will contribute to a resilient agricultural system capable of meeting global food demands while protecting the planet. Whether you’re a smallholder farmer or a large-scale producer, integrating even a few of these methods can make a significant difference. By prioritizing sustainability, we ensure a thriving future for both humanity and the environment



