Irrigation sprinkler systems are essential tools for maintaining healthy landscapes, gardens, and farms. Whether you’re new to irrigation or looking to upgrade your existing setup, understanding the key components and their functions can help you make informed decisions.

Key Components of Irrigation Sprinkler Systems
A typical sprinkler system consists of several interconnected parts. Below are the primary components:
1. Water Source
- Function: Supplies water to the irrigation system.
- Types:
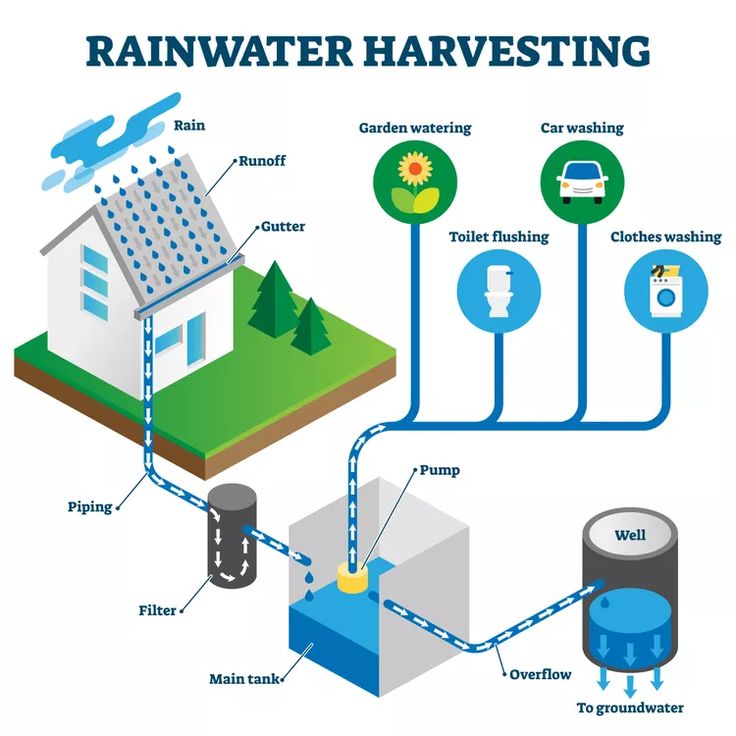
- Municipal water supply.
- Well water.
- Rainwater collection systems.
- Considerations: Ensure the source provides sufficient pressure and quantity for your irrigation needs.
2. Pump
- Function: Draws water from the source and pushes it into the irrigation system.
- Best for:
- Large farms.
- Properties relying on well water.
- Considerations: Choose a pump that matches your system’s pressure and flow rate requirements.
3. Valves
- Function: Control the flow of water to different zones or areas.
- Types:
- Manual valves.
- Automatic valves with timers or controllers.
- Key Role: Ensure even distribution and prevent water wastage.
4. Pipes and Tubing
- Function: Transport water from the source to the sprinkler heads.
- Types:
- PVC pipes for durability.
- Polyethylene tubing for flexibility.
- Installation Tip: Use proper fittings to prevent leaks.
5. Sprinkler Heads
- Function: Dispense water over a designated area.
- Types:
- Fixed spray heads.
- Rotor heads.
- Drip emitters.
- Bubblers.
- Selection Tip: Match the sprinkler type to your area size and vegetation.
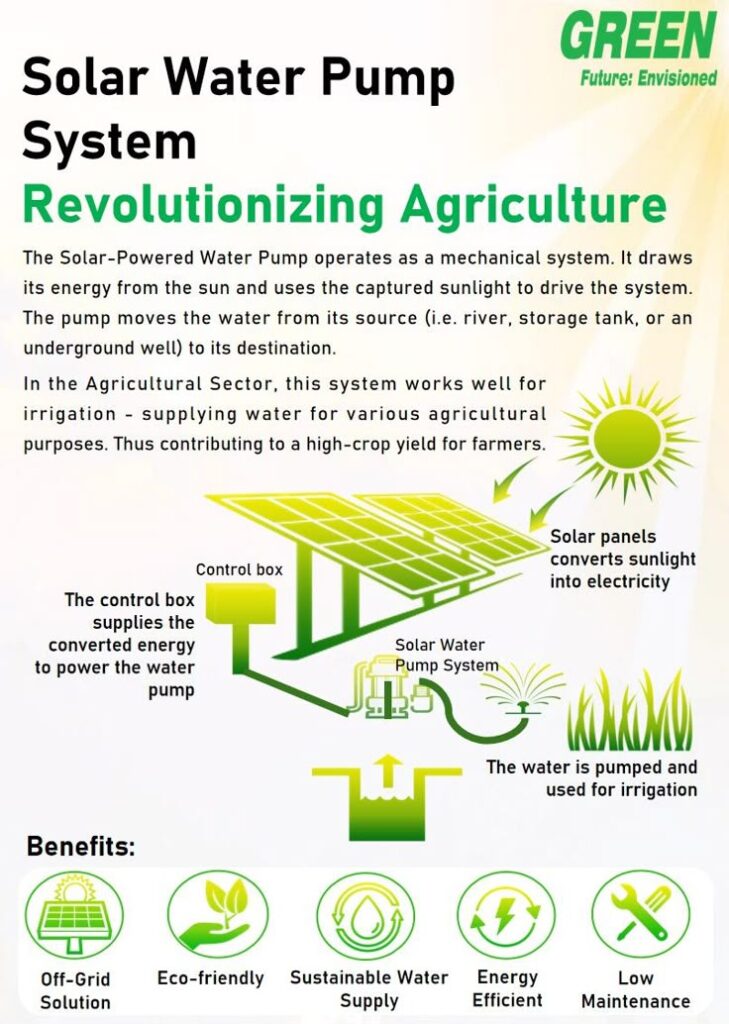
6. Controller
- Function: Automates watering schedules.
- Features:
- Programmable timers.
- Weather sensors for smart irrigation.
- Benefits: Saves time and conserves water.
How These Components Work Together
Understanding how these components function collectively is key to efficient irrigation:
- Water Source and Pump: Water is drawn and pressurized.
- Valves: Direct water to specific zones based on your programming.
- Pipes and Tubing: Transport water without loss or leakage.
- Sprinkler Heads: Disperse water evenly to plants or crops.
- Controller: Automates the process, ensuring timely irrigation.
Functions and Benefits of an Irrigation Sprinkler System
1. Efficient Water Distribution
- Ensures all areas receive adequate water.
- Reduces overwatering and underwatering.
2. Time-Saving Automation
- Eliminates manual watering.
- Smart systems adjust to weather conditions.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
- Lowers water bills by preventing wastage.
- Reduces labor costs on farms.
4. Improved Plant Health
- Provides consistent moisture for optimal growth.
- Prevents diseases caused by irregular watering.
5. Scalability
- Easy to expand systems for larger areas.
- Add zones or upgrade components as needed.
User Tips for Optimal Performance
- Regular Maintenance:
- Check for clogs in sprinkler heads.
- Inspect pipes and fittings for leaks.
- Seasonal Adjustments:
- Modify watering schedules during rainy or dry seasons.
- Winterize your system to prevent freezing damage.
- Smart Upgrades:
- Install rain sensors or weather-based controllers.
- Use drip emitters for water-sensitive plants.
Real-Life User Experiences
Karen, Homeowner: “Automating my sprinkler system has been a lifesaver. I’ve saved hours of manual watering and my lawn has never looked better!”
Tom, Farmer: “Switching to a zone-based system improved irrigation efficiency on my farm. The initial investment paid off quickly in water savings.”
Lisa, Gardener: “Drip irrigation transformed my flower beds. The precise watering reduced weeds and kept my plants thriving.”
Conclusion
Irrigation sprinkler systems are more than just tools; they are investments in landscape and agricultural productivity. By understanding the key components and their roles, you can design or optimize a system that meets your specific needs. Regular maintenance and smart upgrades will ensure your system operates efficiently for years to come.





